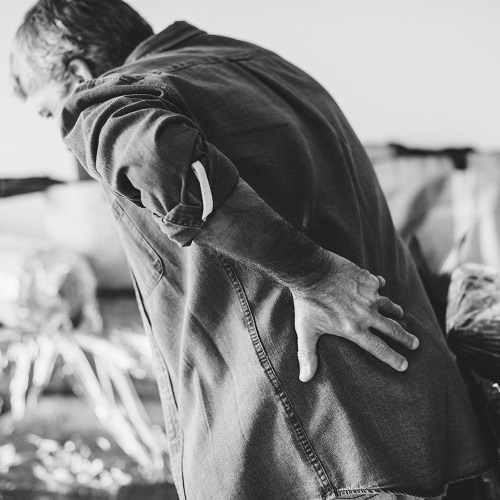
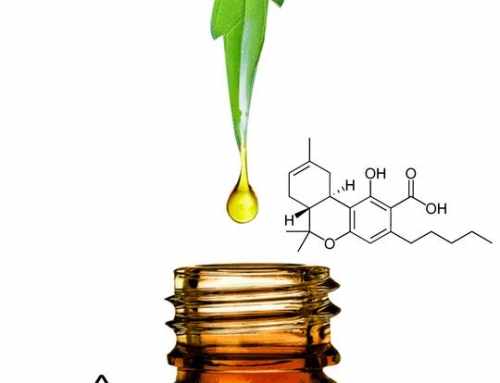
The number one reason people report turning to full spectrum hemp and CBD oil is to relieve pain and inflammation. CBD and other non-intoxicating cannabinoids found in full spectrum hemp oil have proven, in a variety of clinical settings, to be effective therapeutic agents.
Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs traditionally used to treat chronic pain, including neuropathic pain, deliver questionable relief, may invite addiction and can deliver highly adverse side effects such as acute bleeding or even cardiac arrest. There is strong evidence supporting the use of CBD and other nonintoxicating cannabinoids found in hemp to alleviate chronic inflammatory and neuropathic pain without negative side effects.

While studies tend to focus on CB1 and CB2 receptors throughout the brain and body, recent research is demonstrating that cannabinoids, including CBD, do in fact bind to the less studied receptors in the endocannabinoid system. For example, TRPV1 receptors, such as the vanilloid receptor, contribute to non-addictive forms of pain relief. Glycine receptors (GlyRs), specifically the α3 GlyRs, directly suppress pain not only within the central nervous system but also in the ventral tegmental area of the midbrain, the amygdala, the hippocampus and the spinal cord without creating analgesic tolerance. It is the broad body reach without the need for increased doses that is believed to be the main reason why researchers found CBD and related cannabinoids as potential treatments for managing pain associated with spastic episodes in multiple sclerosis and the side effects of chemotherapy.