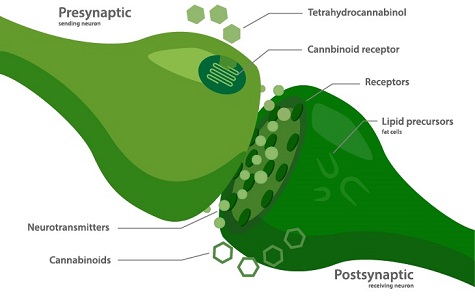
Most of the biological properties related to cannabinoids rely on their interactions with the endocannabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system includes many elements however it is mainly focused on two G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2, as well as two endogenous ligands (natural self-made cannabinoids), anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Cannabinoids like endocannabinoids are thought to play a significant role in a variety of physiological activities including appetite, pain, mood, memory, inflammation, insulin sensitivity and fat and energy metabolism. Focusing on CBD, research has been shown to work in many ways including anti-anxiety, anti-nausea, anti-arthritic, anti-psychotic, anti-inflammatory, and pro immune. CBD has also shown potential as therapeutic agents in diseases such as epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, schizophrenia, multiple sclerosis and affective disorders. Interestingly, CBD also presents strong anti-fungal and anti-bacterial properties, and more interestingly powerful activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).