If you’re familiar with marijuana, you’ve probably heard of THC. It stands for tetrahydrocannabinol, and it’s the chemical ingredient behind that “high” feeling marijuana is known for.
However, THC is just one of over a hundred chemical compounds found naturally in Cannabis. Another one of these compounds is cannabidiol (CBD). CBD has recently become popular, as more people become aware of the many health benefits it provides.
Because they both originate from the Cannabis plant, there’s a lot of confusion around CBD and THC. If THC gets you high, does CBD as well? How are they different? What are the benefits of CBD vs. THC?
In this guide, we break it all down. Keep reading to understand the difference between CBD and THC.
Cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system
We mentioned above that both CBD and THC are chemical compounds naturally found in the cannabis plant. These chemical compounds are properly known as cannabinoids.
When you ingest cannabinoids, they interact with your body’s endocannabinoid system, which is made up of three parts. The first of these are the cannabinoids your body naturally produces. These are called endocannabinoids, with “endo” coming from the word “endogenous” to indicate they are created internally by your body.
The other two elements include the cannabinoid receptors that your body’s endocannabinoids (as well as cannabinoids you ingest) bond with, and the enzymes that break down both the endocannabinoids and cannabinoids.
All of these elements work together to help your body regulate various functions, such as your appetite, immune response, motor control, and feelings of pleasure and pain. Specifically, the endocannabinoid system communicates with your central and peripheral nervous systems to relay messages from your brain to the rest of your body.
Two main types of cannabinoid receptors are critical to this process. These include:
- CB1 receptors: These reside in your central nervous system, including the nerve tissues of your brain and spinal cord.
- CB2 receptors: These reside in your peripheral nervous system, which includes the nerve tissues everywhere else in your body, as well as your digestive and immune system.
Fun fact: The endocannabinoid system was actually named after cannabis, as cannabinoids were discovered before the cannabinoid receptors in our brains.
CBD vs. THC: Effects on the brain and body
CBD and THC are similar to the endocannabinoids your body produces, which is why they’re able to communicate with your cannabinoid receptors. When THC or CBD bind to your cannabinoid receptors, it affects your brain’s release of neurotransmitters, the chemical messengers that send signals between cells in your body.
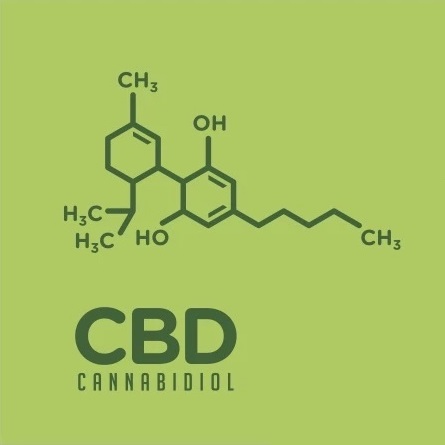
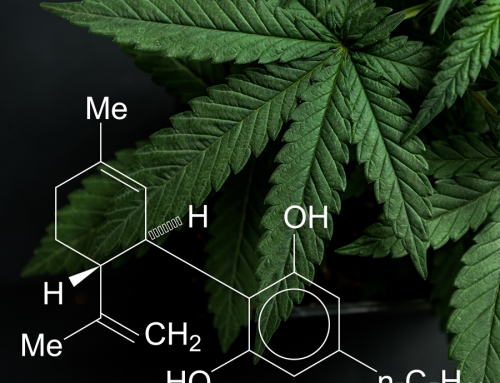
Both CBD and THC have the same molecular formula: C21H30O2. They’re both comprised of 21 carbon atoms, 30 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms. However, they have a different chemical structure:

Because their atoms are arranged differently, THC and CBD interact differently with the CB1 and CB2 receptors in our endocannabinoid system—and as a result, they have different effects on the human body.
THC primarily binds to the CB1 receptors in your brain. This results in the “high” of marijuana and other products high in THC. Besides the high, THC’s focus on the brain also allows it to provide many of the other cerebral benefits of medical marijuana, such as reduced anxiety, pain relief, and improved sleep.
CBD, on the other hand, binds to both kinds of receptors—CB1 and CB2—which are located in your brain and throughout the body. Because it binds to both receptors equally, CBD doesn’t cause the same psychoactive effects of THC. Rather, the effects of CBD are distributed throughout the body, enabling it to benefit various other conditions, like muscle spasms, depression, pain, and inflammation.
Benefits of CBD vs. THC
Because they both bind to CB1 receptors, both CBD and THC can be used to treat many of the same conditions. However, they each have unique uses of their own due to the way they affect different parts of your nervous system.
Below is an overview of the different conditions CBD and THC may treat:

Is CBD or THC dangerous? A review of the side effects
Neither THC or CBD is fatal.
However, due to its psychoactive properties, THC has more side effects, including red eyes, memory loss, and increased heart rate. These may affect the individual temporarily while the drug is still active in their system. For some individuals, THC can also increase anxiety and paranoia.
CBD, on the other hand, has significantly fewer and less intense side effects. It also does not provide the “high” or euphoric feeling of THC, so individuals can experience the health benefits without it interfering with their mental capacity. In fact, CBD can temper some of THC’s potential side effects, such as anxiety or even the high.
Typically, when side effects occur, it is due to other medications the individual is taking and their interaction with the CBD, as opposed to the CBD itself.
How can you use CBD vs. THC?
CBD and THC can both be consumed by the body in a variety of ways, including:
- Orally, either added to food or through a standalone edible, supplement, gel, tincture, or liquid
- Topically, through an oil, lotion, or extract massaged into the skin
- Inhaled through smoke, vapor, or spray
Different strains of Cannabis contain varying amounts of CBD vs. THC. When you purchase a product that contains CBD or THC, it comes from some sort of Cannabis source. Typically, this is either marijuana or hemp.
Marijuana vs. hemp
Marijuana and hemp are two varieties of the Cannabis Sativa plant. While there are more complexities to the differences between marijuana and hemp, essentially it comes down to this:
- Marijuana contains higher amounts of THC, up to 30%, although the average potency is about 12%.
- Industrial hemp contains 0.3% THC or less. Instead, it contains higher amounts of CBD.
THC products are almost exclusively sourced from marijuana. These products are available for purchase only in states where marijuana is legal for recreational or medicinal use (which may require a prescription).
The majority of CBD products are sourced from hemp. It is possible, however, that a CBD product can be sourced from marijuana. Those products tend to have higher amounts of THC, which can be a concern for individuals who either don’t want the psychoactive effects of THC, live in a state where THC isn’t legal, or are providing the product to their child (THC is illegal for anyone under 21). Also, it’s important to note that CBD products sourced from marijuana may cause you to test positive for marijuana use.
When you purchase a CBD product, the label will indicate whether it is sourced from marijuana or hemp. The label will also state whether it is an isolate or full-spectrum CBD product.
- CBD isolates contain no THC whatsoever. CBD isolates are pure CBD which has been extracted in isolation (hence the name) from other cannabinoids in the plant. Due to their concentration of CBD, isolates can have a more pronounced effect on specific bodily systems.
- Full-spectrum CBD, conversely, does contain other cannabinoids from the Cannabis plant, including up to 3% THC. Because they contain more cannabinoids, full-spectrum CBD products tend to enhance the benefits of CBD across the body, rather than targeting a particular system.
Legality of CBD vs. THC
The legality of CBD and THC is in constant flux. As research continues to validate the health benefits of Cannabis, more and more states are legalizing Cannabis in some form.
Currently, marijuana and THC are illegal under federal law. However, a majority of states have legalized marijuana either for medical or recreational use. In the 20 states which have only legalized medical marijuana, users must have a prescription to purchase a THC product. In the 9 states where recreational use is legal, no prescription is required.
If your state has made either medical or both medical and recreational marijuana legal, CBD will also be legal in your state. However, it’s important to ensure it’s legal in your state before purchasing either CBD or THC products. Take a look at the current laws on CBD in your state.
By Heather Davis with CBD Awareness Project