Unlike many of the other bodily systems you know and love, such as your nervous system and the digestive system, the endocannabinoid system (ECS) was only recently discovered, in the early 1990s.
It was discovered so recently, in fact, that it was named after the cannabis plant. That’s because endocannabinoids make up part of the ECS, and they bear a remarkable resemblance to the cannabinoids you find in hemp, marijuana, and other strains of cannabis.
The ECS is also unique in its primary function. Unlike other systems, which focus on specific systems within your body, such as your digestive process, the ECS works to keep all the other systems functioning healthily. This is the main goal of the ECS: healthy homeostasis.
Keep reading to learn how the ECS achieves this important goal. We’ll also discuss how external cannabinoids, like THC and CBD, interact with your body’s own cannabinoid receptors.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The endocannabinoid system is responsible for maintaining your body in a state of optimal homeostasis. In other words, the ECS works to keep your body in a stable condition where everything is working at its best, despite what might be going on outside you.
For example, your ECS aims to keep your heart rate steady and your body temperature within a set range, no matter what the temperature is outside or if you’re working out. If the outside environment forces your body to react, such as by getting hot when you’re exercising in a hot room, your ECS makes you sweat so you can cool back down. Your body is at its healthiest when it’s in a state of equilibrium, so the ECS works with the various systems in your body to maintain this equilibrium.
Three main elements comprise the endocannabinoid system:
- Endocannabinoids: Endocannabinoids are similar to the chemical compounds found in cannabis, such as CBD and THC, which are are called cannabinoids. The prefix “endo” in endocannabinoids stands for endogenous, referring to the fact that these cannabinoids are internally produced by your body. Researchers have identified two main endocannabinoids in the ECS: anandamide and 2-AG.
- Cannabinoid Receptors: Cannabinoid receptors are located on the surface of cells throughout your nervous system and your body. Endocannabinoids, as well as external cannabinoids you ingest, can bond to these receptors, allowing them to communicate with various systems in your body and reset the equilibrium where needed. The two main types of cannabinoid receptors are CB1 and CB2 receptors.
- Enzymes: After the endocannabinoids have bonded to the cannabinoid receptors and served their purpose, enzymes in your ECS work to break them down, preventing them from overcorrecting. Just as there are two endocannabinoids, there are two major enzymes to break them down. FAAH enzymes break down anandamide endocannabinoids, while MAGL enzymes break down 2-AG endocannabinoids.
All of these elements work together to help your endocannabinoid system maintain a state of homeostasis in your body.
What Functions Does the Endocannabinoid System Regulate?
Above, we used an example of overheating while working out, but many biological functions benefit from operating within a healthy range. The endocannabinoid system can help regulate all of these biological functions, including your:
- Appetite and digestion
- Temperature
- Immune function
- Inflammation
- Motor control
- Mood
- Memory
- Sleep
- Pain and pleasure response
The ECS is able to regulate these functions through its communication with the nervous system, digestive system, and immune system—by way of the cannabinoid receptors. Although others exist, to date researchers have focused mainly on two cannabinoid receptors:
- CB1 receptors reside in your central nervous system, which consists of your brain and the nerves in your spinal cord.
- CB2 receptors reside in your peripheral nervous system, which consists of the nerves located throughout the rest of your body (enabling your brain to communicate with these areas), as well as your digestive and immune systems.
Because cannabinoid receptors are located throughout your body, your ECS is able to act with precision whenever it addresses an issue of imbalance in one of your bodily systems. It can pinpoint an area with inflammation and target that issue specifically, rather than affecting other systems and throwing more things out of whack.
How do CBD and THC Affect the Endocannabinoid System?
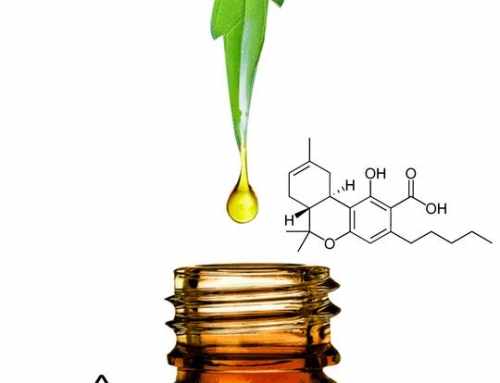
Thanks to our body’s endocannabinoid system, natural cannabinoids from the cannabis plant, such as CBD and THC, can also bind to your cannabinoid receptors and affect your body. However, these two cannabinoids interact differently with your body’s endocannabinoid system.
Like the endocannabinoid anandamide, THC binds with CB1 receptors in your brain. Anandamide has a calming effect on your brain, while THC produces a feeling of being high or stoned. FAAH enzymes can break down anandamide, but they’re not as effective against THC, which is why the “high” sticks around for a longer time.
While THC is known for its high, its focus on CB1 receptors on your brain has other, therapeutic effects related to your brain function, such as insomnia and pain relief.
CBD, on the other hand, can interact with and bind to both types of receptors: the CB1 receptors in your brain as well as the CB2 receptors throughout your body. As a result, and the beneficial effects can be distributed throughout your body, relieving mental conditions like anxiety as well as muscle spasms, pain and inflammation. There’s also no “high” associated with CBD.
CBD also affects your ECS by inhibiting the FAAH enzyme, which breaks down anandamide. Anandamide produces a calming effect, so by blocking the FAAH enzyme that breaks it down, CBD can be helpful in treating anxiety disorders.
Homeostasis plays an important role in our overall health. Since external cannabinoids like CBD can bond to our cannabinoid receptors just as well as the endocannabinoids our bodies naturally produce, researchers are finding that CBD products can have wide-ranging therapeutic benefits for various health issues, including anxiety, insomnia, cancer, and more.
By Heather Davis with CBD Awareness Project